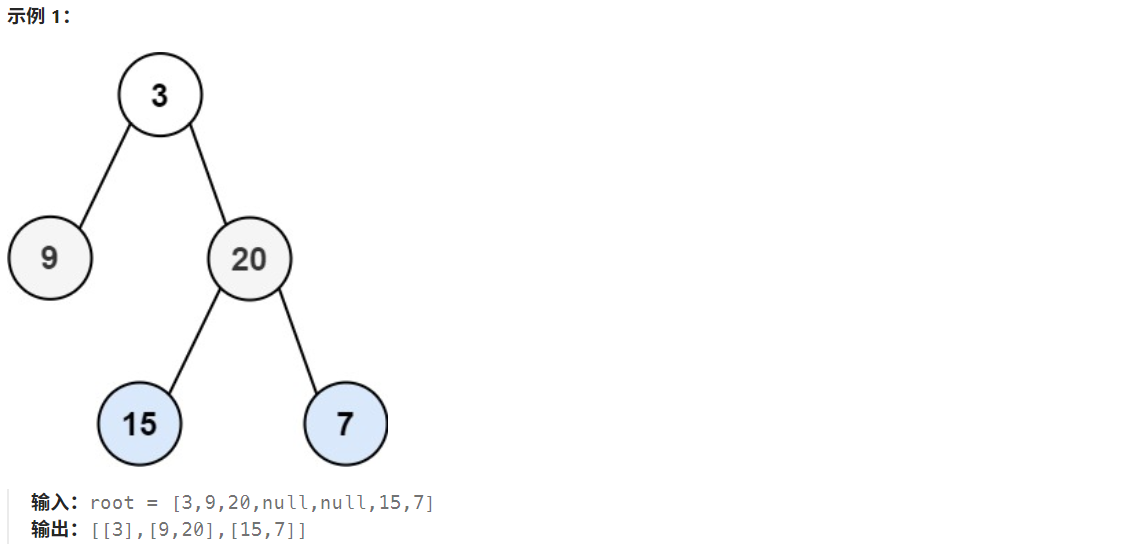
一. 题目


二. 思路
先预处理每个节点的深度。
bfs遍历,每当当前节点和上个进入答案的节点的深度不一样时,新创建List集合存储本层节点。
优化:不用预处理深度,每次统计队列不为空时当前层的个数,然后一次取当前层个数个节点,在取的时候去扩展下层节点。
三. 代码
1. 朴素版
class Solution
{
static final int N = (int) 2e3 + 10;
final List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
final Deque<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>(N);//队列
final Map<TreeNode, Integer> depth = new HashMap<>();//树节点对应的深度
void dfs(TreeNode cur, int d)//预先处理出所有节点对应的深度
{
if (cur == null) return;
depth.put(cur, d);
dfs(cur.left, d + 1);
dfs(cur.right, d + 1);
}
void init(TreeNode root)
{
q.clear();
ans.clear();
depth.clear();
dfs(root, 1);
}
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root)
{
if (root == null) return new ArrayList<>();
init(root);
int pD = -1;//上个加入值的深度
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty())//每次判断当前节点是新一层,还是和上个值是同一层
{
TreeNode cur = q.poll();
int cD = depth.get(cur);//当前节点的深度
if (cur.left != null) q.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) q.offer(cur.right);
if (pD == cD) temp.add(cur.val);
else
{
if (pD != -1) ans.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
pD = cD;
temp.clear();
temp.add(cur.val);
}
}
if (!temp.isEmpty())
ans.add(temp);//最后一层的加入
return ans;
}
}2. 优化版
class Solution
{
static final int N = (int) 2e3 + 10;
final List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
final Deque<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>(N);//队列
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root)
{
if (root == null) return new ArrayList<>();
q.clear();
ans.clear();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
int n = q.size();//当前层的节点个数
List<Integer> tl = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
TreeNode cur = q.poll();
tl.add(cur.val);
if (cur.left != null) q.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) q.offer(cur.right);
}
ans.add(tl);
}
return ans;
}
}